Debt settlement is a financial strategy used to reduce the total amount of debt owed by negotiating with creditors to accept less than the full amount due. It is typically pursued by individuals who are unable to meet their debt obligations and are looking for a way to settle their debts for less than they owe. Although debt settlement can offer a fresh start for those struggling with overwhelming debt, it comes with its own set of risks and challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Debt settlement is a process of negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed.
- Debt settlement can significantly reduce the amount of debt, potentially offering faster resolution.
- Debt settlement may negatively affect your credit score and has tax implications.
- It is most suitable for unsecured debt, such as credit card debt, medical bills, and personal loans.
- Carefully consider all alternatives, such as consolidation or bankruptcy, before opting for debt settlement.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Debt Reduction | Negotiates with creditors to lower the total debt owed, sometimes by 40-60%. |
| Lump-Sum Payment | Typically requires a one-time lump sum payment to settle the debt for less. |
| Unsecured Debt | Primarily for unsecured debts like credit card debt, personal loans, and medical bills. |
| Credit Impact | May negatively impact credit score, as debts are marked “settled for less than owed.” |
| Time Frame | The process can take anywhere from 24 months to 4 years, depending on the debt. |
| Avoids Bankruptcy | Offers an alternative to bankruptcy for those who cannot afford to repay full debts. |
| Debt Settlement Fees | Professional services may charge fees, typically a percentage of the debt reduced. |
| Tax Consequences | Forgiven debt may be considered taxable income by the IRS. |
| Legal Action Risk | Collection agencies may pursue legal action during the settlement process. |
| One Payment to Multiple Creditors | Settles multiple debts with one lump sum, consolidating payments. |

How Debt Settlement Works
- Evaluate Your Debt
Begin by reviewing your financial situation and identifying the debts that are eligible for settlement (usually unsecured debts such as credit cards, medical bills, and personal loans). It’s crucial to know exactly how much you owe and your ability to pay. - Stop Making Payments (If Advised)
In many cases, debt settlement companies advise clients to stop making regular payments to creditors. Instead, you save money in a special account to accumulate funds for the lump-sum settlement offer. However, this step may damage your credit and lead to collection activity. - Hire a Debt Settlement Company or Negotiate Directly
You can either hire a professional debt settlement company or negotiate directly with creditors. Debt settlement companies typically charge fees and will try to negotiate a reduced amount on your behalf. They will attempt to convince creditors to accept a lower amount in exchange for a one-time payment. - Negotiate a Settlement Amount
The goal is to negotiate a reduced debt amount with your creditors. Debt settlement professionals will offer a lump sum (often less than 50% of the total debt) to settle the debt. If the creditors agree, the debt is considered paid in full.
- Save Funds for Settlement
While negotiations are happening, you’ll need to set aside money in a designated account (typically managed by the settlement company). This account accumulates funds until a lump-sum settlement offer is accepted by your creditor. - Make the Lump-Sum Payment
Once a settlement amount is agreed upon, you will make the lump-sum payment. The creditors will then close the debt and mark it as “settled” in your credit report. - Receive Confirmation of Settlement
After payment is made, obtain written confirmation from the creditor that the debt is settled. It is important to ensure that this settlement agreement is documented, as it will help prevent any future issues with the creditor. - Monitor Your Credit Report
It’s essential to review your credit report to ensure that the debt is marked as “settled” or “paid in full” and that it is accurately reflected. However, the settlement may still affect your credit score, and it can stay on your report for up to 7 years.
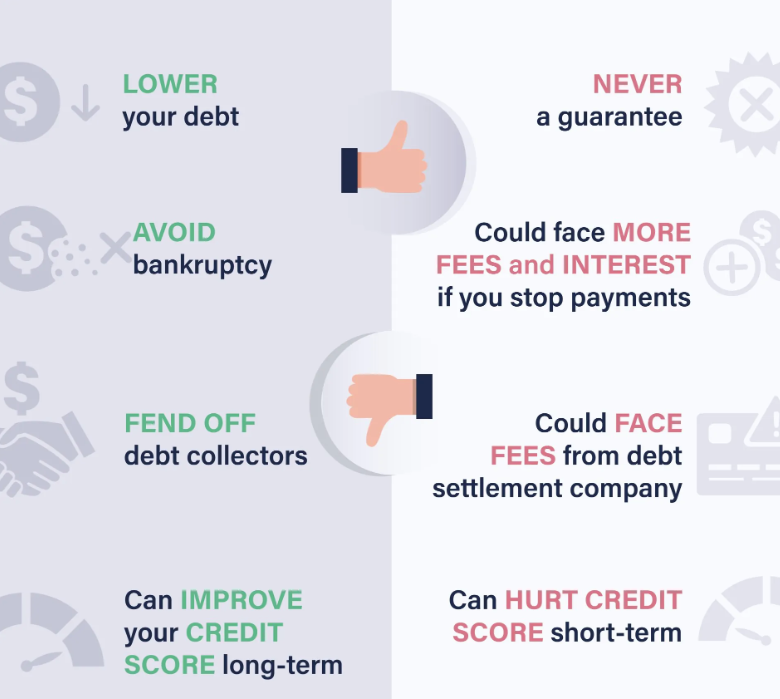
Benefits of Debt Settlement
1. Reduced Total Debt
One of the most significant benefits of debt settlement is the potential to significantly reduce the total amount of debt you owe. In many cases, creditors may agree to accept a lump sum payment that is less than the full amount owed. This reduction can range from 40% to 60%, allowing you to resolve your debt for a fraction of the original balance.
2. Faster Debt Resolution
Debt settlement can expedite the process of becoming debt-free. While traditional repayment plans may take years to pay off, debt settlement allows you to settle multiple debts in a shorter time frame—typically 2 to 4 years. The quicker resolution can relieve financial stress and allow you to focus on rebuilding your financial future.
3. Avoiding Bankruptcy
For individuals who are considering bankruptcy but want to avoid its long-lasting consequences, debt settlement can provide an alternative. While both bankruptcy and debt settlement can negatively impact your credit score, bankruptcy stays on your credit report for up to 10 years, while a settled debt typically remains for 7 years. Debt settlement can be a more manageable option to resolve your financial problems without the permanent consequences of bankruptcy.
4. No Need for Collateral
Unlike secured loans or home equity lines of credit, debt settlement doesn’t require any collateral. This makes it an appealing option for those with unsecured debts such as credit cards, personal loans, and medical bills. Since creditors are often willing to accept less than the full amount owed, they may be more inclined to settle rather than risk receiving nothing if the debtor files for bankruptcy.
5. Relief from Collection Calls and Legal Action
If you’re being harassed by creditors or collection agencies, debt settlement can help stop these collection efforts. By negotiating a settlement, you can reach an agreement with your creditors, reducing the frequency of threatening calls or lawsuits. This provides much-needed relief from the constant pressure and stress of collection activity.
6. Improved Cash Flow
Debt settlement can help free up money that would have otherwise gone toward high monthly payments, especially if you were only making minimum payments. Once your debt is settled, you may have more disposable income to put toward other financial goals such as saving for the future, investing, or building an emergency fund. By resolving large amounts of debt, you can improve your overall financial stability.
7. Prevents Further Damage to Your Credit (When Compared to Bankruptcy)
While debt settlement will still have an impact on your credit score, it can prevent further damage compared to bankruptcy. Bankruptcy can be the last resort when all other options have failed, and it remains on your credit report for much longer. Debt settlement, although it will lower your credit score, is a more viable option for those who wish to avoid the long-term consequences of bankruptcy while still finding a way out of unmanageable debt.
8. Flexibility in Repayment
Debt settlement offers flexibility in terms of repayment options. You may have the opportunity to negotiate a repayment plan that works for your financial situation. In most cases, creditors will be more willing to work with you on a reduced lump-sum payment or an affordable installment agreement, depending on your financial condition.
Risks of Debt Settlement
1. Negative Impact on Credit Score
Debt settlement can significantly damage your credit score. When a debt is settled for less than what was originally owed, creditors report it as “settled for less than full amount” or “paid as agreed.” This notation on your credit report can remain for up to seven years, making it more difficult to secure new credit, loans, or mortgages in the future.
2. Tax Consequences
In many cases, the amount of debt that is forgiven through a debt settlement agreement is considered taxable income by the IRS. For example, if $10,000 of debt is forgiven, you may be required to report it as income and pay taxes on that amount. This tax burden can catch many people off guard, as they may not have planned for the additional financial obligation.
3. Accumulation of Interest and Fees
While you’re negotiating with creditors, your debt may continue to accumulate interest and fees, increasing the total amount owed. If creditors aren’t willing to work with you immediately or if you fail to make agreed-upon payments, the debt may grow larger over time. This can delay the settlement process and result in more financial strain.
4. Risk of Lawsuits and Legal Action
While debt settlement may reduce the amount owed, there is also a risk that creditors may continue or initiate legal action. This could include filing lawsuits, seeking wage garnishment, or attempting to seize assets. During the settlement process, creditors might view you as non-compliant with the original agreement, which may lead them to take legal action.

5. Uncertainty of Settlement Approval
Not all creditors may be willing to settle, and even if they are, there’s no guarantee that a settlement will be reached. Some creditors may demand a higher lump sum than what you can afford or refuse to negotiate altogether. This uncertainty can make debt settlement a lengthy and stressful process, with no guaranteed outcome.
6. High Fees for Debt Settlement Services
Many debt settlement companies charge significant fees for their services, typically a percentage of the debt that is forgiven. While some companies charge only after a successful settlement, others may ask for upfront fees. These fees can add up, potentially leaving you with less money to apply toward your settlement or further complicating your financial situation.
7. Not All Debts Are Eligible for Settlement
Debt settlement is typically only applicable for unsecured debts, such as credit card bills, personal loans, and medical expenses. Secured debts (e.g., mortgages, car loans) cannot be settled in this way because the lender has collateral backing the loan. Additionally, certain debts like student loans, child support, and taxes generally cannot be included in a debt settlement plan.
8. Potential Scams or Unreliable Companies
There are a number of debt settlement companies that may engage in deceptive practices or charge excessive fees for minimal work. It is essential to research and choose a reputable company if you decide to use one. Some companies may make unrealistic promises or fail to negotiate settlements effectively, leading to further financial stress.
When to Consider Debt Settlement
Debt settlement can be a viable option when you find yourself struggling with significant debt. However, it’s important to understand the specific situations in which it may be appropriate. Here are key scenarios when debt settlement might be the right choice:
Overwhelming Debt with No Ability to Pay in Full
If you have large amounts of unsecured debt (such as credit cards or medical bills) and cannot afford to pay the full amount, debt settlement may help reduce the debt. This option becomes relevant if you are unable to meet minimum payments and don’t have enough funds to pay off your debts completely.
Falling Behind on Payments
Debt settlement is often considered when you have missed several payments and cannot catch up. If your creditors are threatening legal action, wage garnishment, or asset repossession, negotiating a settlement might allow you to pay a reduced lump sum and avoid further consequences.
Considering Bankruptcy but Want to Avoid It
If bankruptcy seems like the only option but you want to avoid its long-lasting impact on your credit score, debt settlement could be an alternative. While it can hurt your credit score in the short term, it does not have the long-term effects that bankruptcy has, which stays on your record for 7-10 years.
Unable to Qualify for Debt Consolidation or Management Plans
If you have high amounts of debt and don’t qualify for a debt consolidation loan or a debt management plan (because of poor credit or a lack of stable income), debt settlement may offer a way to resolve your debt without the strict eligibility requirements of other options.
Significant Credit Card or Unsecured Debt
Debt settlement works best for unsecured debt such as credit cards, medical bills, or personal loans. If you have a lot of secured debt (like a mortgage or car loan), debt settlement typically won’t apply, since the creditors have collateral.
Exhausted Other Debt Relief Options
If you’ve already tried negotiating with creditors, using a debt management plan, or consolidating your debts but still find yourself overwhelmed, debt settlement might be the next step to consider. It’s often a last resort after other methods have not worked.
Facing Legal Action or Lawsuits
If creditors have begun taking legal action against you or filed lawsuits due to unpaid debts, debt settlement may help you resolve the issue before it escalates further. Many creditors may prefer settling for less than they are owed, rather than spending additional time and resources on a lawsuit.
You Can Afford a Lump-Sum Payment
For debt settlement to work, you need to be able to pay a lump sum amount, which is often significantly less than what you owe. If you have access to savings or another source of funds that can cover this lump sum, you may be able to negotiate a settlement that resolves your debt more quickly.
Also Read : How Can You Master Debt Management And Achieve Financial Freedom?
Conclusion
Debt settlement can provide significant relief for individuals struggling with overwhelming debt, but it is not without risks. It can reduce the total amount owed and help you avoid bankruptcy, but it may impact your credit score and come with tax implications. If you are considering debt settlement, be sure to weigh the pros and cons carefully and explore other debt relief options before making a decision.
If you choose to pursue debt settlement, working with a reputable debt settlement company or negotiating directly with creditors can help you take the first steps toward financial freedom. Remember to approach debt settlement with a clear understanding of the process, its risks, and the potential benefits to make an informed decision.
FAQs
What is the difference between debt settlement and debt consolidation?
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the amount of debt owed, while debt consolidation combines multiple debts into one payment, often with a lower interest rate.
Can I settle debt on my own without using a company?
Yes, it’s possible to negotiate with creditors on your own. However, many people choose to hire a debt settlement company because of their expertise in negotiating with creditors.
How much of my debt will be forgiven through settlement?
Typically, creditors may agree to forgive 40-60% of the total debt owed. However, the amount forgiven depends on your financial situation and the negotiation process.
Does debt settlement hurt my credit score?
Yes, debt settlement can negatively impact your credit score. Settled debts may appear as “settled for less than full balance” on your credit report, which can lower your score.
How long does it take to settle debt?
The debt settlement process can take anywhere from 24 months to 4 years, depending on the amount of debt, the creditors involved, and how long it takes to reach a settlement.
Are there any tax implications for debt settlement?
Yes, forgiven debt may be considered taxable income. You should consult a tax professional to understand how debt settlement may affect your taxes.
Is debt settlement the best option for everyone?
Debt settlement is not suitable for everyone. It works best for individuals with large amounts of unsecured debt who are struggling to keep up with payments. It should be considered after exploring other options like debt management or consolidation.




